Complete Guide to After Colonoscopy Diet for Better Recovery After undergoing a colonoscopy, it's essential to focus on your recovery diet as it plays a crucial role in healing and restoring your digestive health. A well-planned post-colonoscopy diet can help your body recover effectively, minimize discomfort, and ensure efficient digestion. In this guide, we will explore the best foods to eat...
Effective 3-Month Pre-Bariatric Surgery Diet Plan Embarking on a weight loss journey through bariatric surgery is an impactful decision, often leading to significant health improvements. A well-structured pre-bariatric surgery diet can optimize outcomes and promote sustainable weight loss. The aim of this diet is to prepare your body for surgery while ensuring you develop healthy eating habits. This comprehensive guide will...
Essential Guide to Parakeet Diet for Optimal Health Understanding your parakeet's diet is crucial for promoting its health and happiness. As lively companions, parakeets require a well-balanced and nutritious diet to thrive. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the essential aspects of a parakeet diet for 2025. Knowing how to enhance their nutrition not only improves their lifespan but also their...
Smart Ways to Optimize Your Hashimoto's Diet Plan in 2025 Hashimoto's disease, an autoimmune thyroid disorder, requires careful dietary management to support optimal thyroid function and overall health. In 2025, the focus will be on adopting a Hashimoto's thyroiditis meal plan that aligns with emerging nutritional research and personalized dietary approaches. This article explores essential strategies to optimize your Hashimoto's diet,...
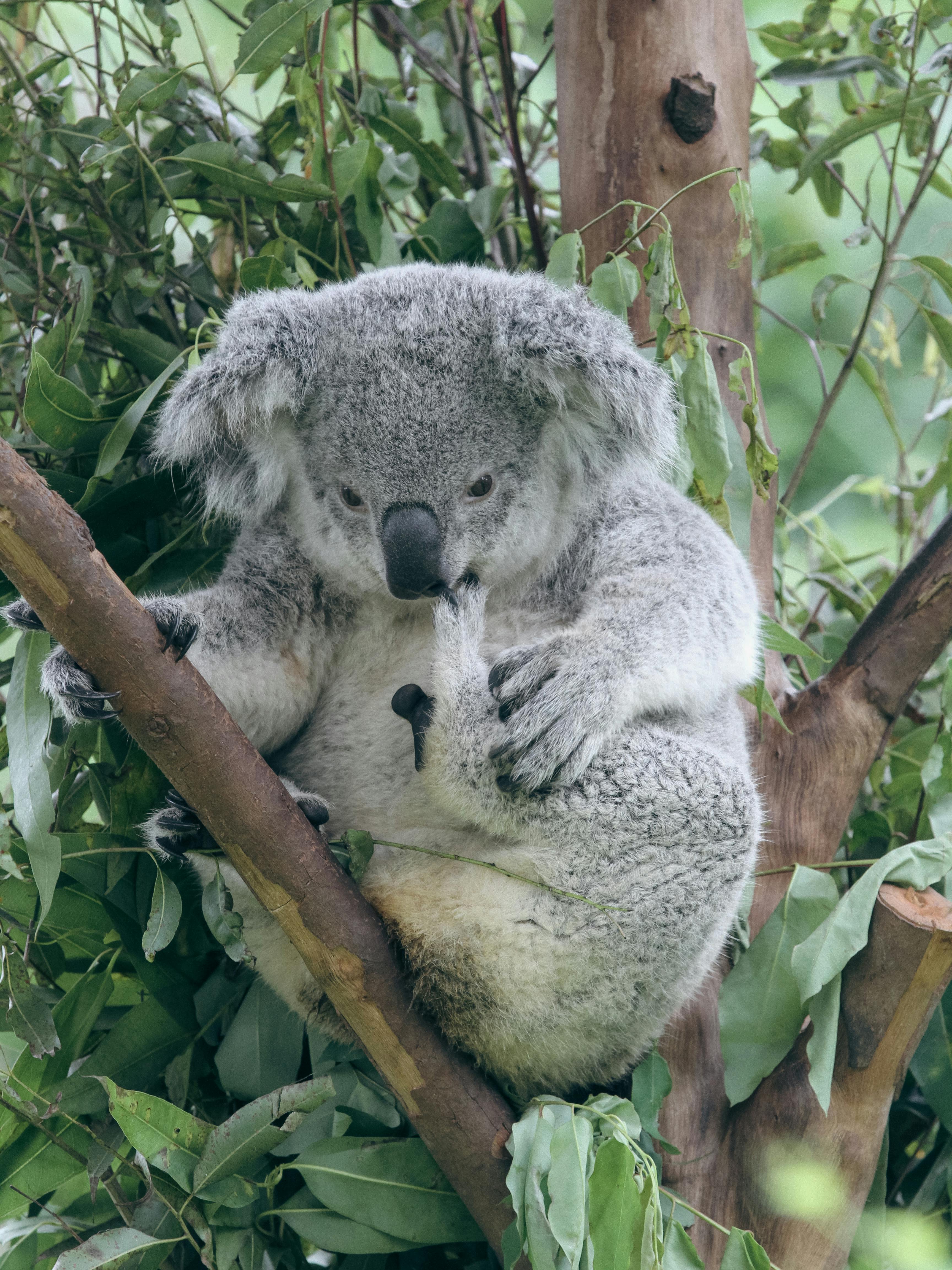
Effective Ways to Optimize Eucalyptus Diet for Koalas in 2025 Understanding the Eucalyptus Diet of Koalas Koalas, being unique marsupials, have highly specialized dietary preferences that hinge almost entirely on eucalyptus leaves. These leaves are not just their primary food source; they play a crucial role in their health and survival. Koalas possess significant adaptations that allow them to thrive on a...
```html Essential Guide to Dog Pancreatitis Diet for Increased Recovery Dog pancreatitis is a potentially serious condition that affects the pancreas, leading to inflammation and digestive issues. Understanding how to manage your dog's diet during recovery is crucial for their health. A well-planned pancreatitis diet can significantly alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and improve your dog's quality of life. In this guide, we...
Essential Guide to Kim Kardashian's Diet for 2025 Success The journey of celebrity diets often captures the attention of fans worldwide, and Kim Kardashian is no exception. Her diet not only reflects her personal preferences but also aligns with broader trends in health and wellness. As we venture into 2025, understanding Kim's dietary habits can provide valuable insights for anyone looking...
The Significance of the Diet of Worms in 1521 The Diet of Worms, held in 1521, was a pivotal moment for the Holy Roman Empire and the broader Protestant Reformation. This imperial council brought together various leaders, including Emperor Charles V, to address the theological issues and political clash sparked by Martin Luther's challenges to established church doctrine. Luther’s Ninety-Five Theses...
Effective Diet Plan for Insulin Resistance Insulin resistance is a condition that affects how your body processes glucose, leading to higher blood sugar levels and potential weight gain. With the rising incidence of insulin resistance globally, particularly in 2025, having an effective diet plan can significantly impact overall health and the ability to manage this condition. An insulin resistance diet focuses...
Best 3 Options for the 7 Day Military Diet to Achieve Results The 7 Day Military Diet is renowned for its potential to deliver fast weight loss results, promising to shed up to 10 pounds in just one week. It operates on a simple principle of calorie restriction and balances meal provisions, providing an effective military diet plan. Participants engage in...