Smart Ways to Optimize Sperm Whale Diet for Better Health in 2025

Sperm Whale Nutrition and Dietary Needs
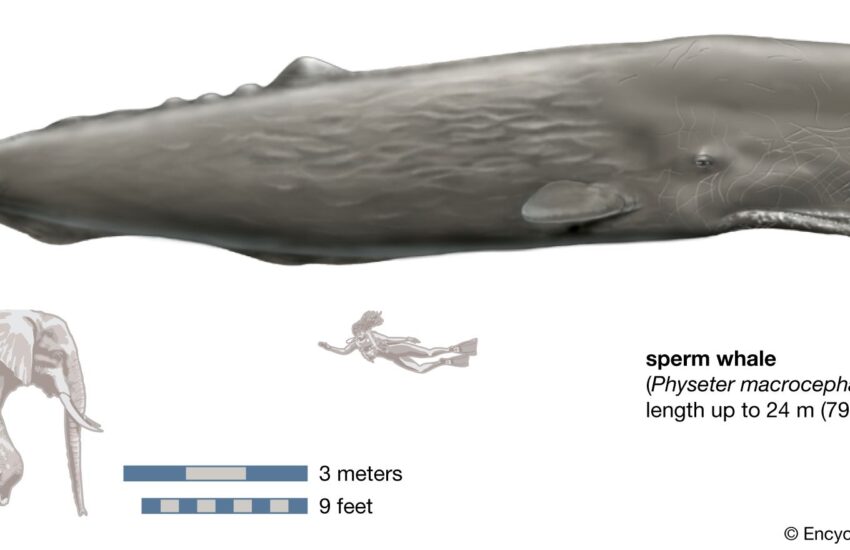
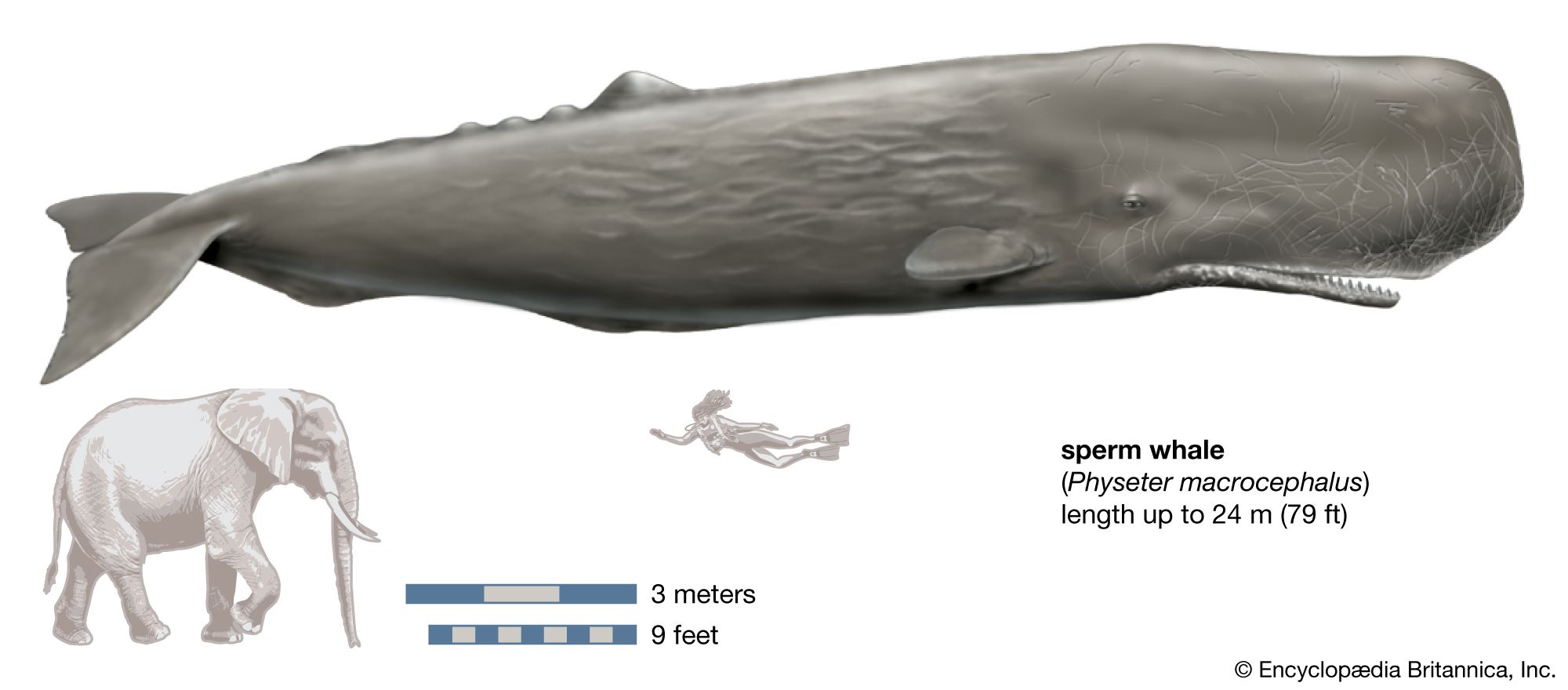
The **sperm whale diet** is a critical aspect of its biological needs. Understanding what do sperm whales eat is essential for marine ecology, especially regarding their role in the ecosystem. The diet of sperm whales primarily consists of squid, deep-sea fish, and other marine organisms. This marine mammal has specific **nutritional needs** that align with its size and energy expenditure, emphasizing the importance of their primary prey of sperm whales. Recent studies have shown that improved understanding and optimization of sperm whale nutrition can enhance their health and resilience in changing marine environments.
Understanding the Feeding Ecology of Sperm Whales
The **feeding ecology of sperm whales** involves complex interactions with marine food sources and ecosystems. Sperm whales mainly target squids, which are rich in nutrients necessary for their large body sizes. **Squid consumption by sperm whales** is not just a dietary choice but a strategic adaptation, as deep-sea squids are plentiful and well-suited for their hunting methods. Moreover, the nutritional importance of fish is noteworthy as sperm whales also consume various fish species, enhancing their **dietary diversity**, which is vital for sustaining a balanced nutrient intake. These feeding habits reflect their position in ocean food chains and help stabilize marine ecosystems by regulating squid populations.
Seasonal Diet Variations in Sperm Whales
One fascinating aspect of the **diet of sperm whales** is the seasonal diet variations due to prey availability and environmental changes. During different times of the year, sperm whale feeding habits may shift depending on the migratory patterns of their prey. Research indicates that in certain seasons, areas may see an increase in specific squid species, leading to a temporary boost in sperm whale populations due to food abundance. By adapting their **feeding strategies** accordingly, sperm whales ensure that they meet their energy requirements effectively, revealing their remarkable adaptability and resilience.
Strategies for Enhancing Sperm Whale Health
To improve the health of sperm whales, it is crucial to focus on their dietary patterns. **Sperm whale diet studies** emphasize optimizing food resources while considering environmental factors that influence prey abundance. By understanding the **impact of climate change on sperm whale diet**, conservation efforts can be tailored to protect and restore habitats crucial for their feeding behavior. Furthermore, addressing human impacts such as pollution and overfishing could improve the **sperm whale eating patterns**, fostering healthier ecosystems that benefit not only whales but the biodiversity of marine life.
Sperm Whale Feeding Habits and Foraging Behavior
Examining the **sperm whale feeding habits** enables researchers to delve into the foraging behavior of this majestic animal. Sperm whales exhibit sophisticated hunting techniques, primarily focusing on **hunting methods** that leverage echolocation to identify viable prey, particularly in deep-sea environments. The characteristics of prey selection highlight their role as apex predators, managing marine ecosystems and influencing prey population dynamics.
The Use of Echolocation in Foraging
Sperm whales utilize unique adaptations such as echolocation for effective foraging. This valuable tool allows them to detect prey even at great depths and in complete darkness, enhancing their **foraging efficiency**. By clicking underwater, they create sound waves that bounce off objects and return information about their environment. This ability is not only crucial for locating their primary food sources, such as squid, but also informs their **dietary habits research** by enabling scientists to gather insights into prey behavior and distribution.
Competition and Cooperation Among Sperm Whales
Social structures appear to play a significant role in **competition for food among sperm whales**. These whales often hunt cooperatively, especially when targeting large prey items, allowing for greater success in capturing substantial quantities of squid and fish. Group hunting behavior not only optimizes their feeding potential but also enables younger whales to learn efficient foraging methods from seasoned individuals. Understanding these dynamics can help researchers devise strategies to protect these species while promoting healthy population levels.
The Role of Prey Characteristics in Nutrition
The characteristics of prey available significantly influence the **nutritional needs of sperm whales**. Different prey items have varying amounts of fat, nutrients, and energy yields; therefore, selective feeding habits are crucial. Studies into **prey availability for sperm whales** consider the depth at which they feed and their targeted prey species, revealing intricate relationships within the marine food web. Recognizing these interactions helps create models that predict changes in sperm whale populations in response to environmental upheavals.
Importance of Sustainable Practices in Ocean Management
Optimizing the **sperm whale diet** extends to broader implications for marine conservation and sustainable fishing practices. The ecological role sperm whales play as top predators creates a balance within marine settings; thus, addressing challenges like overfishing and habitat degradation is vital. Implementing sustainable practices is essential for ensuring **marine resources** remain plentiful and that sperm whales can thrive.
<h3-Strategies for Sustainable Fishing Practices
Fishing practices significantly impact whale populations, with bycatch and depletion effects on their primary prey. Establishing guidelines that combine **sperm whale conservation efforts** with responsible fishing regulations can create a healthier ocean ecosystem. Collaborations among marine bodies, fisheries, and conservation groups have led to developing better practices that minimize harm to whale populations while safeguarding the economic interests of those dependent on fishing.
The Impact of Climate Change on Marine Ecosystems
Climate change has drastic effects on cetaceans, including their **feeding behavior analysis** and overall health. Alterations in ocean temperature, salinity, and currents disrupt prey distribution, affecting **sperm whale feeding ecology**. Understanding these changes fosters informed conversations about policy mechanisms aimed at protecting marine environments crucial for the survival of not just sperm whales but myriad marine species reliant on viable ecosystems.
Community Involvement in Whale Conservation
Community involvement is integral to educational initiatives targeting sperm whale conservation. By advocating for awareness of **marine ecosystem health indicators**, local communities can play a substantial role in protecting sperm whales through monitoring activities and participating in estimated **marine biological studies**. Initiating programs that promote responsible tourism ensures that interaction with sperm whales is done ethically, reducing stress and abuse of their natural habits.
FAQ
1. What are the primary prey of sperm whales?
The **primary prey of sperm whales** includes various squid species, deep-sea fish, and occasionally crustaceans. These foods are high in nutritional content, providing the essential energy that sperm whales require for their size and physiological needs.
2. How do climate change impacts affect sperm whale dietary habits?
Climate change can disrupt the availability and migration patterns of prey species, which influences the **sperm whale dietary habits**. Rising ocean temperatures and changing currents can lead to shifts in the distribution of squid and fish populations, making it more challenging for sperm whales to find food.
3. What role do sperm whales play in the marine ecosystem?
Sperm whales are vital to the **marine food chain and sperm whales**. As apex predators, they help maintain the balance of marine life by controlling squid populations and influencing the dynamics of the ocean food web, which can affect various marine species.
4. How do sperm whale foraging behavior differ from that of other whales?
Sperm whales primarily use echolocation while hunting in deeper waters, which distinguishes their **foraging behavior** from baleen whales that filter feed. This method allows sperm whales to efficiently locate prey in dark deep-sea environments where visibility is limited.
5. What strategies can be implemented to ensure sustainable feeding practices for sperm whales?
Strategies for sustainable feeding practices include enforcing fishing regulations to minimize bycatch, addressing pollution, and engaging in habitat restoration efforts. Advocating for protected marine areas can also create safe environments for **sperm whale food sources**, ensuring their populations remain stable and healthy.
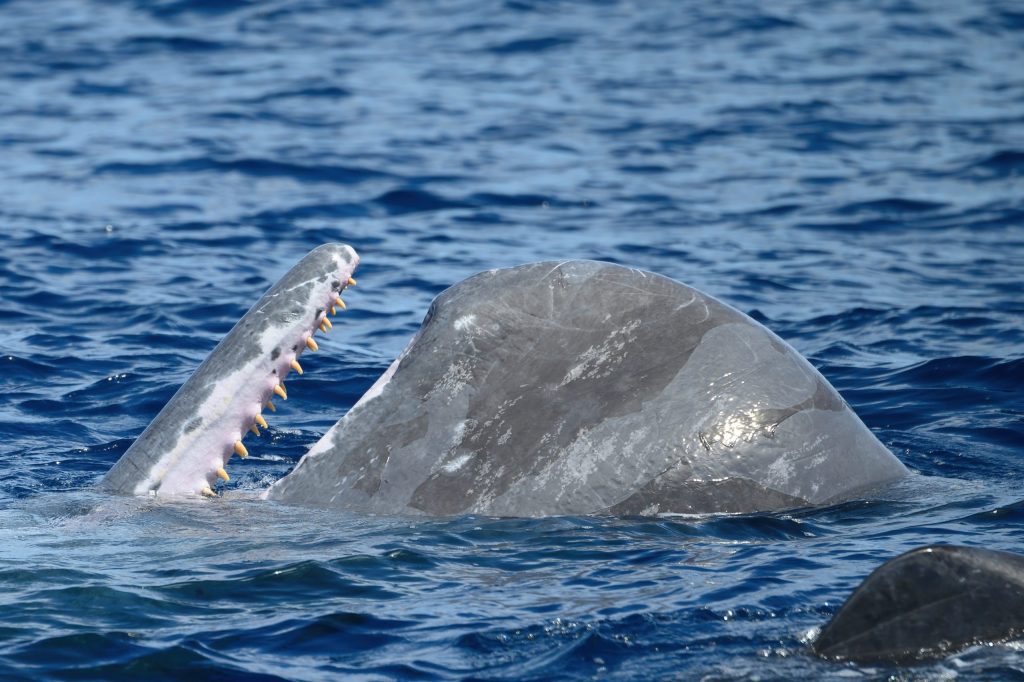
6. How does the structure of sperm whale mouths contribute to their feeding strategy?
The mouth structure of sperm whales is adapted to manage their specific feeding methods. They have large teeth in the lower jaw that aid in gripping slippery prey like squid, while their streamlined mouth design allows for efficient movement through water during dives.
7. What research methods are used to study sperm whale diets?
Researchers utilize various methods to study **sperm whale diet**, including analyzing stomach contents of stranded whales, performing acoustical monitoring to observe feeding behaviors, and conducting long-term dietary studies through tagging and tracking efforts. These approaches provide valuable insights into their eating patterns and prey preferences.
By understanding these aspects of **sperm whale nutrition and diet**, researchers and conservationists can promote strategies to enhance the health of sperm whales and their ecosystems moving forward into 2025 and beyond.