Effective Ways to Manage Irritable Bowel Syndrome with a High Fiber Diet
Understanding Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Dietary Fibers
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder affecting millions worldwide. Managing IBS symptoms effectively requires a multifaceted approach, and a **high fiber diet** has proven beneficial. Dietary fibers can be classified into two main types: **soluble fiber** and **insoluble fiber**. Soluble fiber dissolves in water, forming a gel-like substance that aids in controlling blood sugar and cholesterol levels. On the other hand, insoluble fiber remains intact, promoting regular bowel movements and relieving constipation. By understanding their roles, individuals can tailor their nutrition to improve gastrointestinal health and enhance **digestion improvement**.
The Role of Fibers in Digestion
Dietary fibers are critical in maintaining a healthy digestive system. They help bulk up stool and facilitate regular bowel movements, which can be especially beneficial for those dealing with **IBS symptoms relief**. **Fiber-rich foods** such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables not only ease the passage of waste but also serve as prebiotics, promoting a healthy gut microbiome. This improved balance of gut bacteria can alleviate symptoms such as excessive gas and bloating. Specifically, integrating **soluble fiber** sources like oats and chia seeds nourishes beneficial bacteria, potentially reducing **IBS flare-ups**.
High Fiber Foods for IBS Management
A well-rounded **gut-friendly diet** rich in dietary fibers can include a variety of foods. Some great options are whole grains (like quinoa and barley), fibrous vegetables (such as broccoli, carrots, and Brussels sprouts), and beans or legumes. **Fruits for IBS**, like bananas and berries, provide essential vitamins while adding soluble fiber to the diet. Incorporating these foods into daily meals can turn simple dishes into high-fiber breakfasts, snacks, and dinner solutions, balancing taste and nutrient intake effectively.
Fiber Sources and Cooking Techniques
When preparing meals for a high-fiber diet, using the right **cooking methods for high fiber foods** can enhance nutrient absorption and the overall digestion process. Steaming vegetables or cooking grains will keep most of their nutritional value intact. Combining **fermented fibers** with a good cooking technique can support higher fiber intake, making them more digestible. Additionally, adding herbs, spices, or a healthy fat source can flavor dishes while also providing substantial health benefits.
Meal Planning and Dietary Changes for IBS
Effective management of IBS often begins with careful meal planning. Developing a **balanced diet for IBS** involves incorporating a variety of **fiber sources** while being mindful of potential IBS trigger foods. Keeping a food diary can help individuals track their reactions and tailor their diet accordingly. Integrating **hydration for fiber diet** is paramount; drinking enough water enables fiber to work effectively, assisting in smoother digestion and nutrient uptake.
Creating High Fiber Meal Ideas
Planning **meal ideas for IBS** should prioritize high fiber choices that do not aggravate symptoms. Breakfast might include oatmeal topped with chia seeds and berries; lunch can consist of a chickpea salad with plenty of greens; and dinner could showcase grilled salmon paired with quinoa and steamed broccoli. Experimenting with **high fiber recipes** can make meal prep both enjoyable and satisfying, allowing individuals to explore various **vegetables for digestive health**.
Snacking Wisely with Fiber
Healthy snacking can never be overlooked in a **high fiber diet**. Options like hummus with carrot sticks, apple slices with almond butter, or a small bowl of mixed nuts can provide quick energy while ensuring fiber intake stays high. Such **snacks for high fiber diet** are not just beneficial for digestion; they keep cravings at bay and maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day, promoting overall wellness.
Natural Remedies and Probiotics for IBS
In addition to fiber, certain **natural remedies for IBS**, like probiotics, can play a vital role in managing the condition. Probiotics help improve the microbiome’s balance, contributing to effective digestion. Foods like yogurt and fermented vegetables can be excellent additions. Combining fiber and probiotics creates a supportive environment for gut health, leading to fewer IBS-related challenges and enhanced **gut health tips**.
Understanding Fiber and Probiotics Interaction
The interplay between **probiotics and fiber** can enhance digestive health significantly. When fibers reach the intestines, they serve as nourishment for the probiotics, fostering their growth. This process maximizes the benefits of both. Studies have shown that increasing both dietary fibers and probiotics can lead to improved symptoms and enhance the **healthy gut microbiome**. This symbiotic relationship presents a clear opportunity for those experiencing chronic digestive issues to find more efficient ways to manage their condition.
Hydration in the High Fiber Diet
Implementing a **high fiber diet** necessitates adequate **hydration for fiber diet**. With increased fiber intake, drinking plenty of water is essential to prevent dehydration and ensure that the digestive system functions optimally. The general recommendation is to consume at least eight glasses of water daily, but this can be adjusted based on factors such as physical activity, climate, and individual health needs. Proper hydration works synergistically with dietary fibers to support bowel health and minimize constipation.
Key Takeaways
- A **high fiber diet** plays a crucial role in managing **IBS** by enhancing digestion and alleviating symptoms.
- Incorporating both **soluble** and **insoluble fiber** into meals can improve gut health and lessen IBS flare-ups.
- Effective meal planning, smart snacking, and hydration are essential components of a successful IBS dietary strategy.
- The combination of **dietary fibers** and probiotics is beneficial for maintaining a balanced gut microbiome.
- Understanding individual triggers and adjusting dietary choices will facilitate better management of IBS symptoms.
FAQ
1. How does a high fiber diet specifically relieve IBS symptoms?
A **high fiber diet** aids in alleviating IBS symptoms by promoting regular bowel movements and enhancing overall digestion. Soluble fibers help retain water in the intestines, creating a gel-like substance that eases stool passage. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from **constipation** associated with IBS. In contrast, insoluble fibers add bulk to the stool, promoting quicker transit through the digestive tract, which can help prevent **IBS flare-ups**.
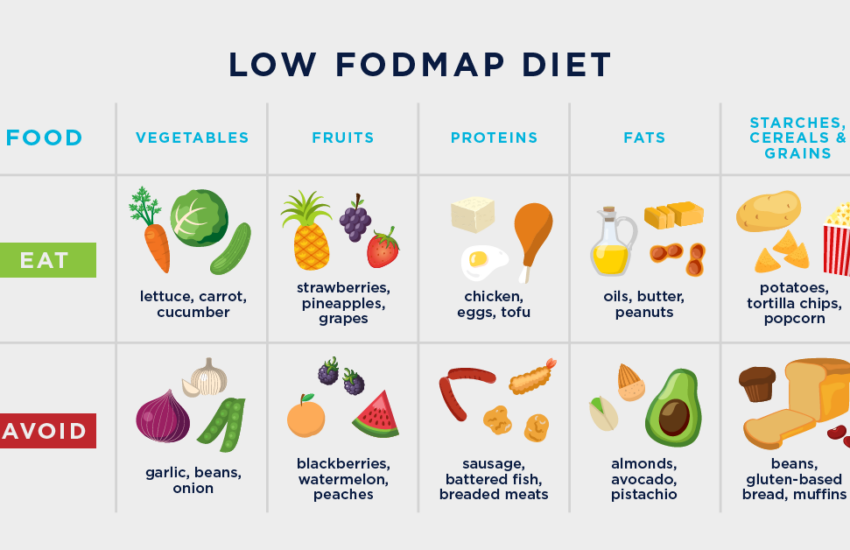
2. What are some effective **fiber sources** for those on a **low FODMAP diet**?
For individuals following a **low FODMAP diet**, effective **fiber sources** include gluten-free whole grains like quinoa and brown rice, leafy greens (such as spinach and kale), and certain fruits, including bananas and oranges. These options provide beneficial **dietary fibers** without triggering symptoms. Incorporating **lower FODMAP fibrous vegetables** like carrots and potatoes can also contribute to overall fiber intake without adverse effects.
3. Can fiber supplements be beneficial for IBS management?
Yes, **fiber supplements** can be beneficial for IBS management when dietary fiber intake is insufficient through food alone. Supplements, such as psyllium husk, offer soluble fiber that can help regulate bowel function. They should, however, be introduced gradually to minimize potential **gastrointestinal discomfort** often associated with sudden increases in fiber intake. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement, especially for managing IBS.
4. What are the benefits of high fiber foods for overall health?
High fiber foods offer numerous health benefits beyond alleviating IBS symptoms. They can help regulate cholesterol and blood sugar levels, support weight management, and contribute to improved digestive health. Additionally, a higher fiber intake is linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular issues and certain types of cancer. Therefore, exploring various **fiber-rich foods** can enhance holistic well-being.
5. How can I incorporate more fiber into my daily meals?
Incorporating more fiber into daily meals can be achieved by gradually adding high-fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. Start your day with a **high fiber breakfast** like oatmeal topped with berries. Opt for whole grain bread for sandwiches and include a variety of **vegetables for digestive health** in your meals. Planning meals that feature beans, seeds, and healthy snacks like nuts can also increase your intake. Consistency and creativity in cooking can significantly enhance your **fiber intake recommendations**.
6. Should I consider a **gluten-free fiber** option for my diet?
Considering a **gluten-free fiber option** may be beneficial for those who experience sensitivities to gluten, even if they do not have celiac disease. Many gluten-free grains like quinoa, buckwheat, and rice are excellent fiber sources, promoting gastrointestinal health while minimizing **IBS symptoms**. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before significantly altering your diet to ensure it meets nutritional needs while addressing digestive concerns.
7. Are there foods to avoid that may worsen IBS symptoms?
Certain foods can act as triggers exacerbating **IBS symptoms**. Common offenders include high-fat and fried foods, dairy products (for those with lactose intolerance), and foods high in **FODMAPs** such as certain fruits, onions, and wheat. Monitoring and identifying personal triggers is crucial to managing and maintaining a **gut-friendly diet** effectively.
For a more in-depth understanding of natural remedies and dietary strategies for IBS management, visit here or explore additional recipes and tips here.