Smart Ways to Optimize Your GERD Diet Plan for Better Digestion in 2025

Managing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) through a well-planned diet can significantly improve your digestive health and overall well-being. In 2025, adopting **smart dietary changes for GERD** is essential for alleviating symptoms and enhancing quality of life. This article delves into effective strategies for creating a **GERD diet**, featuring **reflux-friendly meals**, nutritious recipes, and vital meal planning tips that prioritize relief from **GERD symptoms**.
Understanding GERD Diet and Its Importance
Recognizing the significance of a specific diet in managing GERD is crucial. A **GERD diet** is tailored to reduce acidity and avoid trigger foods that lead to symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation. Implementing **dietary changes for GERD** not only alleviates discomfort but also fosters long-term digestive health. Incorporating **healthy eating for acid reflux** can be a game-changer, leading to better management of GERD across various lifestyles and preferences.
Status Quo: Common GERD Symptoms
GERD symptoms typically include heartburn, regurgitation, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing. While many individuals can relate to these experiences, understanding the triggers behind symptoms can pave the way for effective **symptom relief diet**. Using a **GERD foods list** as a guideline can help eliminate foods that commonly cause flare-ups, such as spicy dishes, fatty meals, and caffeine. By replacing these with **digestive health foods**, you can enhance your overall health while minimizing disruptive symptoms.
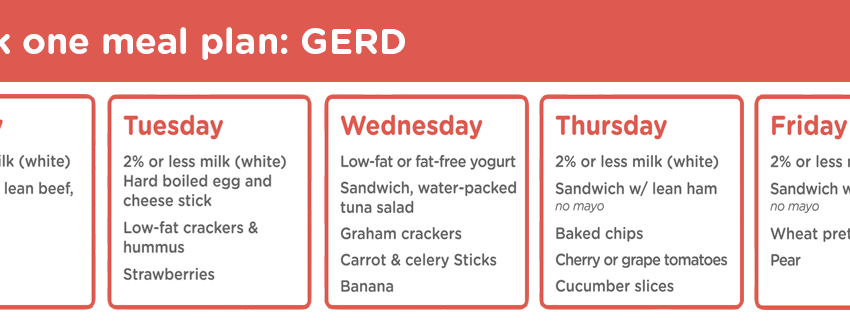
Building Your GERD-Friendly Meal Plan
Creating a comprehensive **GERD meal planning** approach involves carefully selecting foods and meals that provide nutritional balance while avoiding common triggers. Prioritize **low-acid recipes** that include a variety of non-citrus fruits such as bananas and melons, alongside vegetables like leafy greens and asparagus. Including whole grains like oats and quinoa can also sustain digestive health. Opt for **protein sources for GERD**, such as lean meats or plant-based proteins, that are less likely to aggravate symptoms.
Portion Control and Meal Timing
Another crucial element in optimizing your GERD diet is to practice proper portion control and mindful eating. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can reduce the pressure on the stomach and minimize instances of acid reflux. Additionally, timing your meals wisely—allowing at least three hours between the last meal and bedtime—can help prevent nighttime symptoms. Identifying optimal **meal frequency for GERD** will enhance your digestive experience without overwhelming your system.
Foods to Include and Avoid for GERD
Understanding the difference between **foods to avoid with GERD** and those that promote healing is vital. Incorporating **best foods for reflux**, such as almonds, oatmeal, and ginger, can offer gentle support to the digestive tract. Conversely, steering clear of highly processed foods, caffeine, chocolate, and acidic items significantly improves the quality of your diet.
Creating Reflux-Friendly Meals
Crafting **reflux-friendly meals** can be effortless with creative exploration. Start with simple, **GERD-friendly recipes** that inspire comfort without escalating symptoms. For instance, a simple dish of baked chicken breast seasoned with herbs, served along with steamed vegetables and quinoa, exemplifies a fulfilling meal. **Cooking for GERD** often entails using techniques such as steaming or baking, avoiding frying, which tends to introduce unnecessary fats often harmful to those with acid reflux.
Minimizing Food Sensitivities
Everyone’s body reacts differently to various foods. Keeping a **food diary for GERD** can assist in recognizing **food sensitivities GERD**. Take note of which meals may lead to discomfort and adjust your diet accordingly. This personal reflection offers valuable insights and can help streamline future meal prep, reducing the risk of unintentionally consuming problematic ingredients.
Alternative Beverages for GERD Management
Incorporating appropriate beverages is just as important as solid food choices. Instead of opting for high-caffeine or carbonated drinks, aim for **GERD safe beverages** like herbal teas and alkaline water, which can benefit overall digestive health. Consider hydration’s role in regulating your digestion while also acknowledging the substances that provoke acid reflux to make more informed choices.
Smart Cooking Techniques for GERD
The methods you use to prepare food can also affect GERD symptoms. Adopting **cooking techniques for reflux** can preserve the nutritional value of ingredients while ensuring they are less prone to trigger symptoms. For instance, slow cooking and poaching are excellent options for retaining moisture without introducing unnecessary fats.
Incorporating Probiotics
Integrating probiotics into your GERD diet can improve gut health and digestion. Yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods introduce beneficial bacteria to your gut, potentially easing **GERD symptoms relief**. Including these in meals or snacks not only creates flavorful options but also supports a versatile diet.
Herbal Remedies and Supplements
Exploring **herbal remedies for GERD** can provide additional support for managing symptoms naturally. Herbs like chamomile, slippery elm, and licorice root can offer soothing properties for irritated stomach lining. Moreover, considering supplements in conjunction with your diet can be beneficial; however, seeking **professional guidance for GERD** is vital in ensuring safety and compatibility with treatment plans.
Key Takeaways for Your GERD Diet Plan
To achieve a successful **GERD diet**, here are some essential points:
- Focus on **low-acid recipes** and **reflux-friendly meals**.
- Avoid common triggers, such as fatty, spicy, and caffeinated foods.
- Explore a range of **GERD-friendly snacks** and **healthy eating for acid reflux**.
- Utilize **cooking techniques for reflux** to maintain nutritional integrity.
- Incorporate hydration and mindful eating habits into your daily routine.
By diligently applying these strategies, you can craft a **GERD meal plan** that optimizes your health in 2025 and beyond.
FAQ
1. What are the best foods to include in a GERD diet?
In a GERD diet, aim for non-citrus fruits like bananas and apples, low-fat proteins such as chicken and fish, and complex carbohydrates like whole grains and oats. Incorporating **nutritious meals for GERD** aids digestion and promotes symptom relief.
2. How can portion control affect GERD symptoms?
Practicing portion control can mitigate GERD symptoms by reducing the pressure within the stomach. Smaller, more frequent meals can help prevent overloading the digestive system, leading to better overall management of acid reflux.
3. What are some **healthy snacks for GERD**?
Great snacks for GERD include carrots with hummus, oatmeal, or yogurt with berries. These **GERD-friendly snacks** nourish while avoiding potential triggers, making snacking a positive part of your dietary plan.
4. Can cooking techniques influence acid reflux symptoms?
Yes, utilizing gentle cooking techniques such as steaming, baking, or broiling minimizes the introduction of high fats and encourages healthier meals, which is particularly important when aiming to **manage GERD through diet**.
5. What are herbal remedies that may help with GERD?
Herbal remedies like chamomile tea, slippery elm, and ginger may ease GERD symptoms. Always consult a healthcare provider when considering these **herbal remedies for GERD** to ensure they don’t interact with any ongoing treatments.
6. How important is hydration for GERD?
Staying properly hydrated is vital, as it assists in digestion and can help break down food efficiently. Opting for **GERD safe beverages** like herbal teas and water can support your digestive health while avoiding irritants.
7. Is mindful eating beneficial for GERD?
Absolutely! **Mindful eating for acid reflux** encourages awareness of your eating habits, helping you avoid overeating and recognize foods that could trigger symptoms. This practice fosters a healthier relationship with food and promotes better digestion.