Effective Ways to Optimize Your Gastroparesis Diet for Better Digestion in 2025

Managing gastroparesis can be challenging, but by focusing on a tailored gastroparesis diet, individuals can see improvements in their digestion and overall well-being. This condition, marked by slow gastric emptying, demands thoughtful dietary adjustments. In this guide, we explore effective strategies, meal planning tips, and food recommendations to optimize your diet for better digestion in 2025.
Essential Guidelines for a Low-Fiber Diet
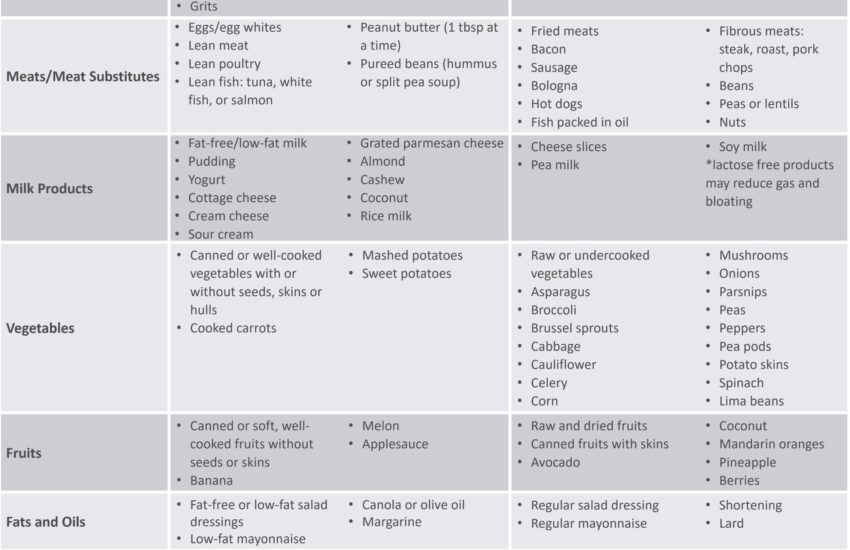
Transitioning to a low-fiber diet is crucial for those with gastroparesis as it aids in simplifying digestion. Foods high in fiber can be harder to break down, leading to increased discomfort. Instead, focus on easily digestible options such as bananas, white rice, or refined grains. Incorporating cooked vegetables rather than raw can also make fiber more tolerable. It’s important to monitor individual reactions to different foods; keep a food journal to identify what works for you.
Implementing Small Frequent Meals
Instead of three large meals, adopting the practice of eating small frequent meals can significantly benefit digestion. This approach helps maintain nutrient intake without overwhelming the digestive system. Aim for 5-6 small meals throughout the day that include a balance of macronutrients and focus on easy-to-digest foods. Planning meals based on your body’s signals can foster healthier eating habits and reduce symptoms.
Volume Control and Portion Sizes
Paying attention to portion sizes is vital when dealing with gastroparesis. Since the stomach’s ability to process large quantities is impaired, consuming smaller portions helps prevent discomfort and bloating. Additionally, opt for nutrient-dense foods like high-calorie foods or calorie-dense snacks that are easy to digest. For example, a high-protein shake serves as an excellent option that delivers energy without overwhelming the system.
Food Choices for Digestive Comfort
Choosing the right foods can have a profound impact on symptom management. Focus on incorporating bland foods and soft foods, which are typically easier on the stomach. Items like mashed potatoes, smooth peanut butter, and smoothies can ensure nourishment while promoting digestive comfort. Keep experimenting with easy-to-digest foods to find what your body tolerates best.
Nausea Relief Strategies
Nausea is a common concern among those with gastroparesis. Opt for foods that provide nausea relief, such as ginger teas or peppermint. Ensuring proper hydration through sips of water or electrolyte solutions is also an essential aspect of hydration management. These small adjustments can greatly reduce the frequent bouts of nausea that interfere with daily activities.
Managing Dietary Fats and Food Intolerances
Understanding diets low in fats and identifying any food intolerances is key for effective symptom control. Fatty foods are harder to digest and can slow down gastric emptying. Keep dietary fats low and prioritize cooking methods, such as steaming, that promote easier digestion. Always consider potential food intolerances, including gluten or lactose, and make necessary adjustments in your meal plan.
Meal Planning and Preparation Tips
Cohesive meal planning is crucial for maintaining a successful gastroparesis diet. Consider creating a weekly meal schedule to stay organized. Integrate cooking methods that focus on preparing soft foods, such as slow-cooking methods for stews and soups. Additionally, meal service options can be explored, providing convenience while ensuring nutritional requirements are met.
Choosing Safe Foods and Emergency Snacks
Establishing a list of safe foods that your body handles well aids in quick meal decisions. Develop easy recipes that fit within your dietary guidelines. Keep healthy snacks, such as nutritional supplements or high-calorie snacks, readily available in case of emergencies. This preparedness helps to prevent sudden hunger pains, which can lead to poor food choices.
Strategies for Dining Out and Social Situations
Eating out can be tricky, but understanding what options are available can facilitate a smoother experience. When dining at restaurants, opt for simple modifications—such as requesting gluten-free options or sauces on the side. Engaging in discussions with staff about your dietary restrictions will enable tailored food preparation, which can help mitigate symptoms during social gatherings.
Nutrition Education and Support Resources
Recognizing the importance of ongoing nutrition education in gastroparesis management can yield long-term benefits. Engaging with a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance for implementing therapeutic diets. Further resources, such as community support or online forums, can connect you with individuals facing similar challenges, fostering a sense of camaraderie while promoting healthier eating habits.
Consultation with Dietitians and Specialists
Regular check-ins with health care providers and dietitians can significantly enhance your management plan. Patient care in gastroparesis often requires dietary adjustments as individual needs change. Building a strong support network through medical advisers, along with peer support, can ensure you maintain a balanced approach to your diet while coping with the challenges of gastroparesis.
Tracking Symptoms and Food Reactions
Monitoring your body’s response to different foods through a meal journal offers critical insight into your condition. Pay attention to the psycho-emotional impact of your diet and how different meals affect your overall health. With time, you’ll discover which food combinations or nutritional strategies work best for your unique needs.
Key Takeaways
- Embrace a low-fiber diet focusing on digestible foods.
- Implement small frequent meals to ease the digestive process.
- Prioritize bland and soft foods for digestive comfort.
- Plan meals ahead and keep healthy snacks available to manage hunger.
- Seek support through consultation with dietitians and engage in ongoing nutrition education.
FAQ
1. What are some effective hydration tips for managing gastroparesis?
Staying hydrated is crucial. Sip fluids throughout the day instead of consuming large amounts at once. Options like electrolyte drinks or smoothies can also help to maintain hydration levels while providing nutrients that support digestion.
2. How do I identify food intolerances related to gastroparesis?
To identify food intolerances, journal food intake and symptoms. Gradually eliminating potential trigger foods, such as gluten or dairy, can aid in determining which items may exacerbate symptoms, allowing you to make informed dietary choices.
3. Can I include vegetarian options in my gastroparesis diet?
Yes, vegetarian options can certainly fit within a gastroparesis-friendly diet. Incorporate easily digestible, soft vegetarian foods, such as mashed beans, smoothies, and cooked grains. Ensure nutritional needs are met by consulting a dietitian.
4. What are some examples of comfort foods suitable for gastroparesis?
Suitable <comfort foods> include mashed potatoes, broth-based soups, oatmeal, and yogurt. These options promote ease of digestion and can provide the sense of comfort often associated with traditional meals.
5. How can I find support for managing my chronic condition?
Engaging in online communities, support groups, or consultations with healthcare providers can offer invaluable resources and encouragement. Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges fosters a sense of solidarity and provides helpful coping strategies.
6. What is the importance of meal frequency for gastroparesis?
Increased meal frequency, via small and frequent meals, helps prevent overwhelming the digestive system, making it essential for better digestion and symptom control. Frequent meals minimize the risk of nausea and fullness, allowing adequate nutrient absorption.
7. Are there specific cooking methods best suited for a gastroparesis diet?
Cooking methods like steaming, boiling, and slow-cooking are optimal for preparing soft and digestible meals. These techniques help retain nutrients while enhancing the texture of the food, making it easier on the stomach.